|
Bigfoot is a large, bipedal ape species that has been seen in North America for centuries. The name "Bigfoot" was coined in the late 50's by a journalist in CA describing large tracks found at a logging site. Another name for this animal is "Sasquatch," which is an anglicized version of the Coast Salish word "se'sxac," meaning, wild men. The evolutionary origins of Bigfoot are widely debated, however, evidence shows close ties to humans & other great apes.
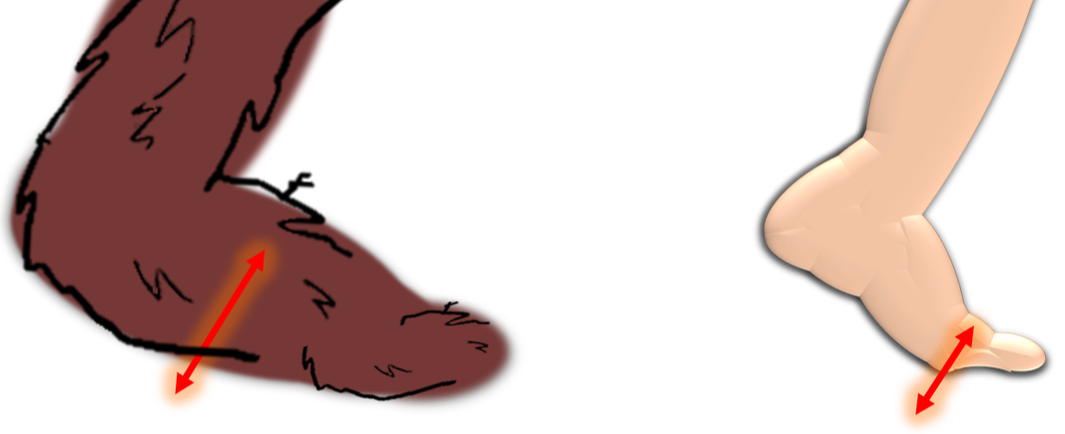
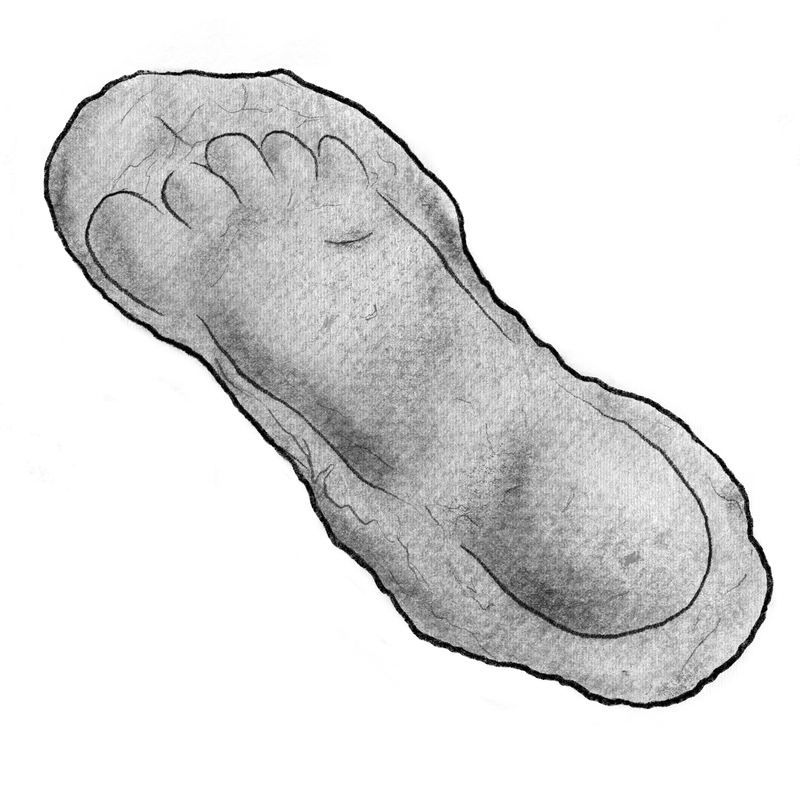
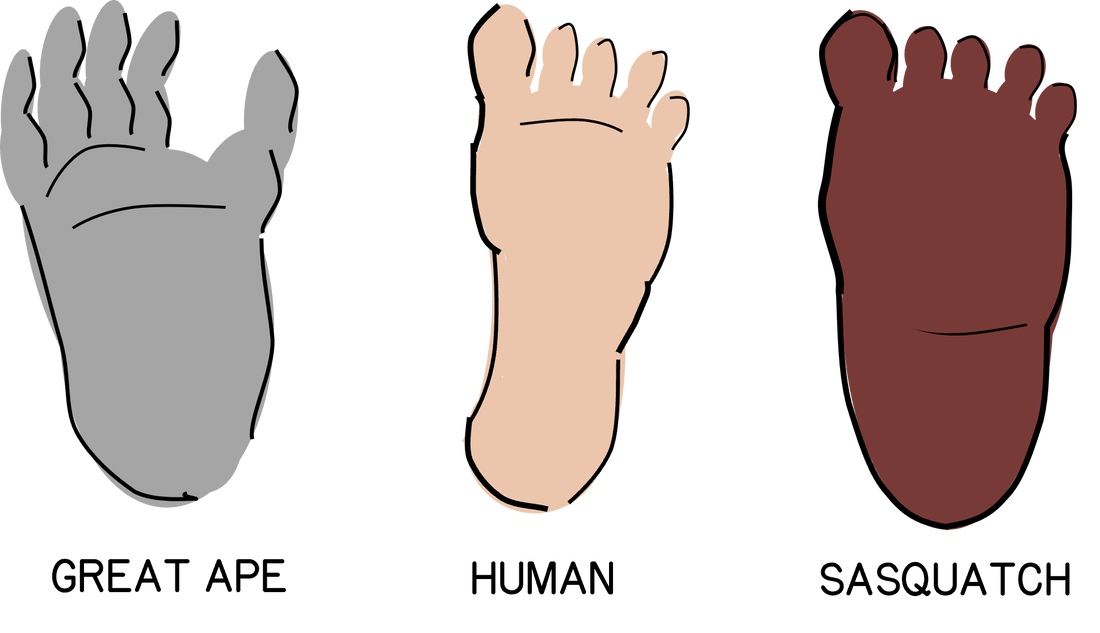
After close examination of hundreds of credible footprints, scientists have been clued in to why the creature walks the way it does. A human has a longitudinal arch, which means the entire foot is incorporated into the lever which propels it off of the ground, & weight is pushed to the ball of the foot. The bending happens at the toes, providing traction. In a foot with midfoot flexibility, the weight is not concentrated on the ball of the foot, but rather the midfoot.
Red arrows represent where the foot bends
Midfoot flexibility causes weight to transfer from rear to forefront & is most commonly present in apes. This anatomy shows itself in the form of a midtarsal break within footprints. The midtarsal break is a feature of the print that occurs when the midfoot bends, causing the dirt or sand to lift up into a small mound in the middle of the footprint.
Although midfoot flexibility is attributed to apes, Sasquatch footprints also suggest human anatomy in the form of an aligned big toe. Other great apes have a divergent big toe, which is used for climbing. Humans & Sasquatch have transitioned to bipedalism, causing their big toe to align with the other toes as their need for climbing trees has diminished.
In addition to footprints, hair samples have also been analyzed & determined to originate from an unknown ape. Dr.Jeff Meldrum & Dr. Henner Fahrenbach examined unknown hair samples to determine their origin. In order to identify a species, scientists observe overlapping scales, which can be different in color & thickness, diameter of the hair, cross-sectional shape, & length of the hair shaft. Human hair grows differently & longer than other species, therefore showing characteristics such as a cut end & distinctive follicle structure. After Fahrenbach gathered nearly a dozen samples that were not linked to any known animal, the two scientists began studying their similarities.
Their findings were interesting in that two of the samples had the same structural characteristics, making them the same species, however their hair color & hair length varied, as it does in Homo sapiens. Although the samples were ultimately inconclusive, they did point to the probability of a relict hominoid species, with origin that resembles both humans & other great apes.
Native Americans have stories of Sasquatch dating back thousands of years. "Sasquatch" is an anglicized version of the Coast Salish word "se'sxac," meaning wild men. Almost every group across North America has a name for this species & they are often depicted in indigenous art!
Type your location in the search bar to find a Sasquatch report near you!
|
Because of the tough competition between Homo sapiens & other hominoids, the Bigfoot species seems to have adapted to avoid us humans. Here's some behavior you can expect from Sasquatch:
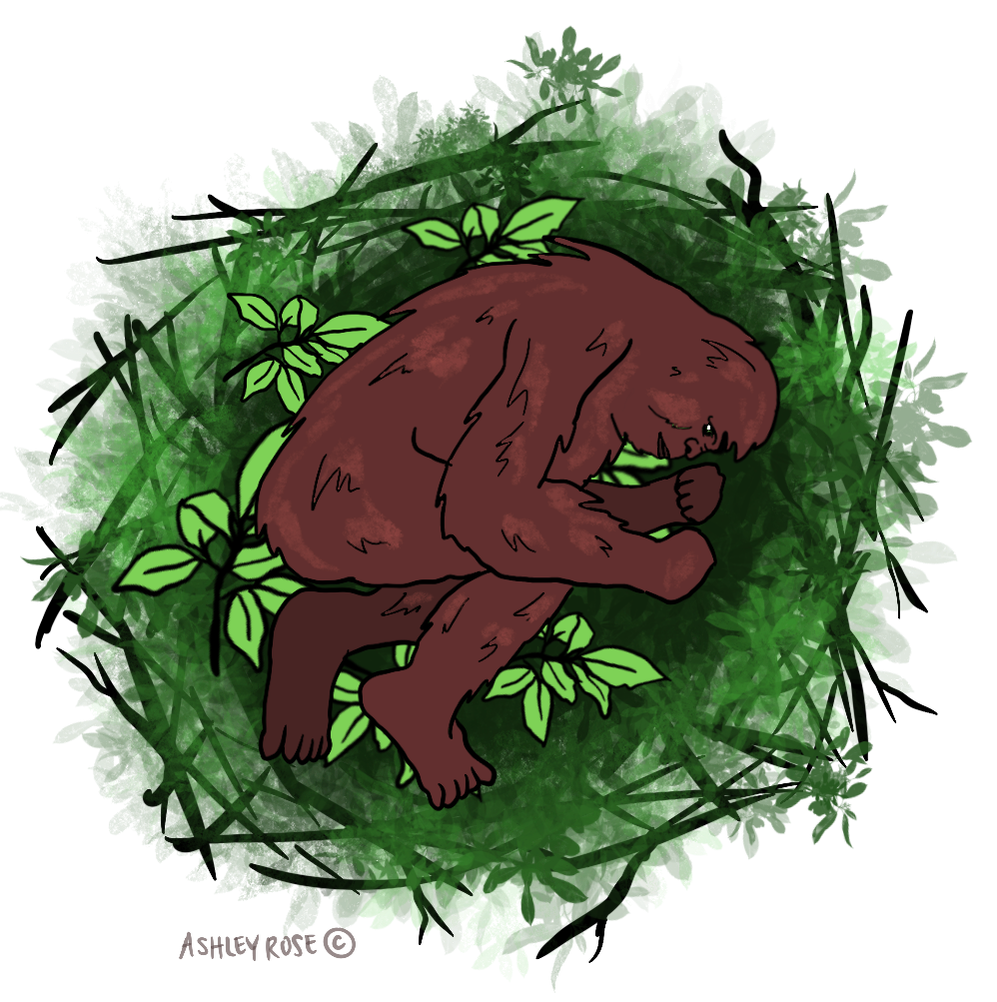
Evidence strongly suggests that Sasquatch sleeps on the ground just like us humans. The Olympic Project of Washington has documented several nesting sites containing over 20 ground nests that resemble those of known apes & measure between 4-9 feet. Hair samples collected from the nests do not match any known species, but display the same structural uniqueness found in other Sasquatch hairs. Between credible eye-witness reports, ground nesting sites & no evidence of nesting in trees, we can conclude that Sasquatch spends their time sleeping on the ground.
According to Why We Sleep by Matthew Walker, English scientist & professor of neuroscience & psychology at the University of California, Berkeley, sleep is essential to intelligence, memory function, & evolution. Why are we smarter than other primates? It may just have something to do with sleep. REM, or Rapid Eye Movement sleep, is a deep paralysis that boosts social complexity & cognitive intelligence. Because primates sleep in trees, they cannot achieve REM sleep, as the sleep paralysis would cause them to fall to their death. Humans spend 20-25% of our sleep in the REM state, compared to a 9% average across other primates. Other apes sleep longer, but we sleep deeper, leaving us more time for social learning & innovation! What does this mean? If modern humans evolved our social complexity & cognitive intelligence through REM sleep, Sasquatch may have too! Bigfoots have been reported to range in color, size & stature. There are males, females & juveniles, just like any other species!
On October 20th, 1967, Roger Patterson & Bob Gimlin headed out on horseback to Bluff Creek, California, as part of a search for this species. After spending about 2 weeks in the field, Roger captured a one-minute film of a Sasquatch. What sets this footage apart is the muscle structure observed with each of the creature's movements, her pendulous breasts, & the footprints she left behind. To this day, the Patterson Gimlin footage has remained the most credible evidence of this species, as attempts to prove it a hoax have failed. The individual in the film, nicknamed, "Patty" is estimated to stand between 6-7 feet tall. About 9 days after the footage was shot, a taxidermist/tracker named Bob Titmus cast 10 of Patty's footprints that had been well preserved in the sand. These prints offer insight into the anatomy of this species, as they show midfoot flexibility in the form of a midtarsal break, a detail that wouldn't be discovered for another 30 years.
Sasquatch are opportunistic hunters & have been seen eating everything from deer, to berries, to leaves, to small mammals to fish & more. There have even been reports of them dumpster diving!
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
|
Emily's evidence
|
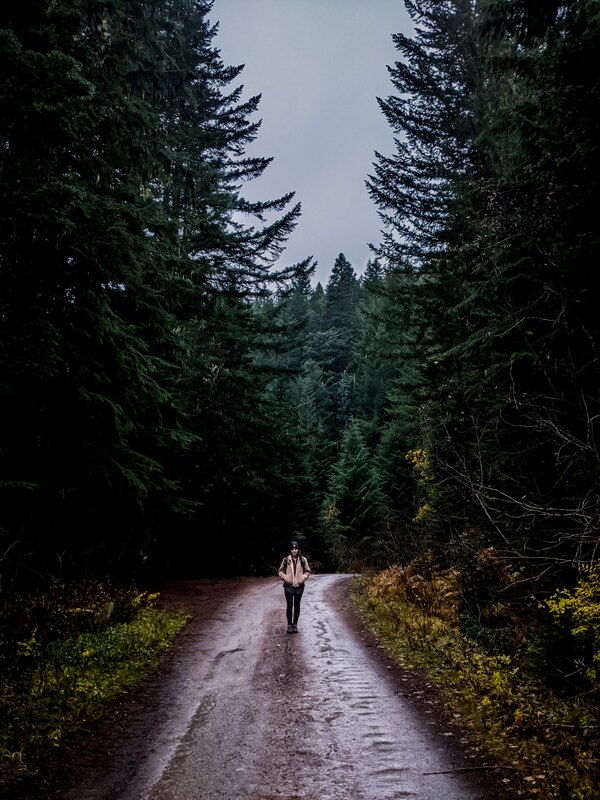
Many people ask me if I have encountered Sasquatch myself, & the answer is, yes! In the fall of 2021, I was working on a short-term research project in Mt. Hood National Forest, where I experienced several encounters with Sasquatch. One night, while conducting field research on private property, I heard a loud crack & a huge tree being pushed over. Shortly after that, my research partner & I were peering into the tree line. The moonlight was very bright, creating a blueish hue that filled the gaps between trees. As I was studying the forest, I saw the tree gap directly in front of me close, as a large, human-shaped shadow passed between the trees. I returned to the area & measured the branch that was closest to its head, putting the figure at 7' tall. Moments after my sighting, my research partner turned to me & said "Did you just see that?" Turns out we both saw the same figure, from different angles. Being that it was dark & backlit, I did not get a look at its features, only the unmistakable shape of its body, towering over mine. Despite this being a visual sighting, the most credible encounter to have, I was actually more excited by another experience.
my favorite encounterVocalizations, smells & knocks are often difficult to be sure of, but when they all happen just minutes apart, a connection can be placed. After entering the valley, my partner & I heard a clacking noise. It was loud, with no particular rhythm to it. It definitely sounded different than a woodpecker or person. My first thought was that something was trying to break open a nut! We took cover behind some rocks & listened for about 20 minutes. We decided to crawl closer to the tree line to see if we could find the source of the noise. As soon as we moved, the clacking stopped. At that point, we knew whatever it was had seen us, so we stood up, & casually walked towards the source. As we approached the tree line, we noticed a strong musky odor, & a beautiful pink rock sitting on a tree stump. We later identified the rock to be a big chunk of salt. All around the stump was a lingering smell. I would compare it to the smell of ape enclosures at the zoo, mixed with a cow farm. As I entered the tree line, I immediately heard a loud knock, coming from around the same area as the clacking. Then, another knock from the opposite tree line answered. At that point, we retreated to a small cluster of trees in the middle of the valley. As we whispered about our next strategy, we were interrupted by a noise that jolted my entire body. It was a huff, similar to the noise a gorilla makes when it is intimidating someone. I had considered a grizzly bear at the time, because the noise was just so loud, it had to be within feet of us. But I did not see anything standing there, so I figured it could have been a bear growling behind some bushes. However, there are no grizzly bears in Oregon. Looking back, I wonder if the Sasquatch was down on all fours, or up in a tree, which is why I didn't see it. The noise prompted us to leave & regroup.
|
Best heard with headphones
The next night, we set out on a drive through the deepest parts of the forest. The old logging roads were spectacular, & it felt like we were driving through Jurassic Park. After a few hours of exploring, & not seeing another soul in sight, we decided to stop the car & replicate some Sasquatch howls in an attempt to elicit a response. My partner howled, & immediately after, we heard a high pitched howl. The howl was unlike anything I've ever experienced & the power behind it was incredible. Some coyotes were set off, which was actually perfect, because I was able to contrast the howl I just heard with that of the dogs. Completely, utterly, different! After the coyotes died down, another high pitched howl struck my ears. And then, a low howl boomed from the creek below the ridge we were parked on. Wow, wow, wow! I had just heard 3 Sasquatch. Amid my excitement I couldn't help but recall an experience I had in Lake George, NY in 2017. I heard the same high-pitched howls, & this really excited me. Sasquatch behavior is consistent across North America, & this experience was an important confirmation of that. Although I saw one on a different occasion, I lend more attention to this particular experience, because I was close enough to smell one & heard them clear as day, all within 48 hours. I am so fortunate to have experienced this & it was a major motivator for my continued field work.
Best heard with headphones
My most recent encounter actually took place behind my house. I know, it's pretty funny that I travel to all these wilderness areas, just to experience something right in my own backyard! It's actually the last place I would have expected activity to take place, well, because, that would just be too good to be true! Turns out, there is quite a lot of privately owned, swampy forest behind the perimeters of my rental cottage, & I was caught off guard when I heard these vocalizations while enjoying a fire pit in the fall of 2023.
where's your footage?So you've read about my encounters & you're wondering where my pictures are if I've seen one! The simple answer is that it's just not that easy to snap a picture of a Sasquatch! Let's break it down:
how can i do better?I always like to ask myself how I can better my skills & further my research. Documentation is so important, so I've decided to allocate funds from my souvenir sales to pay for better audio equipment, a new dash camera & a GoPro to strap to my chest during field outings. I now know that I must be prepared at all times to see or hear a Sasquatch!
|